From Refractory Organics to High Salinity: How Nanobubbles Solve Industrial Wastewater's Toughest Challenges
Against the backdrop of rapid industrial development, industrial wastewater is becoming increasingly complex in composition, with prominent issues such as refractory organic compounds, high salinity, and high organic load. Traditional treatment processes are confronted with challenges including low mass transfer efficiency, incomplete pollutant removal, and high operational energy consumption.
The ultra-fine nanobubble generation technology developed by Sinokle Technology is an innovative and highly efficient water treatment technology. Endowed with its unique physicochemical properties, it demonstrates remarkable advantages in wastewater treatment processes, providing a high-performance solution for the advanced treatment of industrial wastewater. By generating tiny bubbles with diameters at the micrometer or even nanometer scale, this technology achieves breakthroughs in enhancing mass transfer efficiency, strengthening pollutant degradation, and expanding process adaptability, thus effectively overcoming the technical bottlenecks of traditional wastewater treatment methods.
I. Core Technical Advantages: Unique Properties of Ultra-fine Nanobubbles
Compared with conventional bubbles, ultra-fine nanobubbles boast distinct physicochemical advantages, laying a solid foundation for the upgrading of wastewater treatment processes:
1. Ultra-high specific surface area
With small diameters and dense distribution, ultra-fine nanobubbles have a far higher specific surface area per unit volume than conventional bubbles. This significantly expands the gas-liquid contact area, providing ample interfacial conditions for the reactions between pollutants, oxidants, and microorganisms.
2. Superior mass transfer efficiency
Bubbles rise slowly in water with a long residence time, and they possess a self-compression property. This enables them to continuously release dissolved oxygen or other gases into the water body, greatly improving gas solubility and solving the core problem of low gas-liquid mass transfer efficiency in traditional processes.
3. Stable existence period
Affected by surface charges, ultra-fine nanobubbles are not prone to coalescence. They can stably exist in water for several hours or even longer, ensuring the continuity and adequacy of reactions.
4. In-situ generation of reactive species
During the rupture of ultra-fine nanobubbles, a local high-temperature and high-pressure environment is created, triggering the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). These active substances can directly oxidize and decompose refractory organic compounds, enhancing the pollutant removal effect.
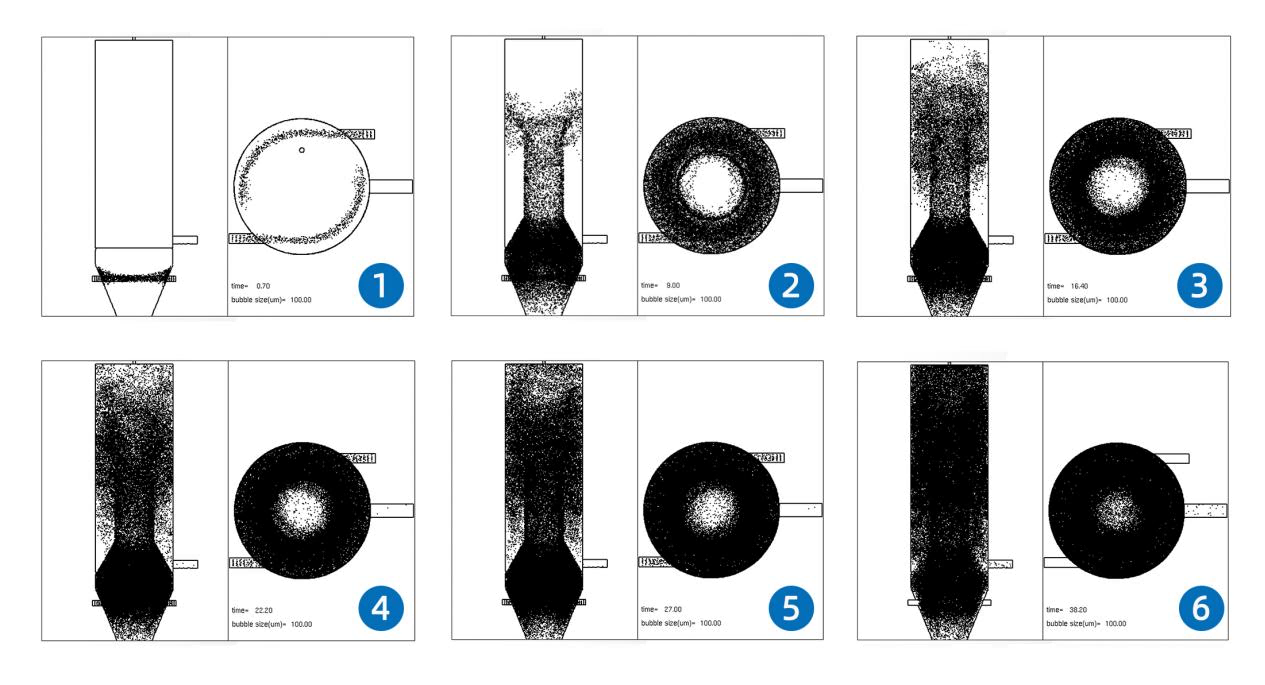
PiC 1. Generation of Micro-bubbles
II. Multi-dimensional Positive Effects on Wastewater Treatment Processes
For refractory organic wastewater generated from industries such as pharmaceuticals, petrochemicals and printing and dyeing, the ultra-fine nanobubble generation technology can enhance treatment efficacy through a dual-action mechanism.
On the one hand, the abundant dissolved oxygen provides favorable conditions for advanced oxidation processes (e.g., ozonation), improving oxidant utilization efficiency, facilitating the generation and transfer of reactive species such as hydroxyl radicals, and accelerating the oxidative decomposition of refractory pollutants including benzene series, antibiotics and chlorinated organics. On the other hand, the strong oxidizing properties of ultra-fine nanobubbles can directly attack the key structures of pollutants, avoiding the problem of increased toxicity caused by the accumulation of intermediate products.
The high-salinity environment in industrial wastewater (e.g., reverse osmosis concentrate with TDS up to 58,000 mg/L and above) tends to inhibit the performance of traditional treatment processes, whereas the ultra-fine nanobubble technology demonstrates exceptional water quality adaptability. For high-salinity wastewater, the reactive substances generated by ultra-fine nanobubbles can effectively decompose chlorinated organics. Meanwhile, it avoids the inhibitory effect of salt ions on catalysts or microorganisms in conventional processes, maintaining stable treatment performance even after continuous operation for several days, with a far lower activity attenuation rate than that of conventional processes.
For high organic load wastewater (e.g., ethylene wastewater from petrochemical enterprises with COD ranging from 1,500 to 2,000 mg/L), the high-efficiency mass transfer property of ultra-fine nanobubbles can rapidly supply sufficient oxygen or oxidants to the reaction system, improving COD removal efficiency. In comparison with traditional processes, the introduction of this technology increases COD removal rate from 42% to 83% and benzene series removal rate from 51% to 95%, significantly reducing pollutant load.
Traditional wastewater treatment processes (e.g., ozonation) suffer from drawbacks such as high energy consumption per ton of water and substantial oxidant consumption. In contrast, the ultra-fine nanobubble technology achieves dual reductions in energy consumption and chemical dosage by optimizing mass transfer efficiency, thus realizing energy conservation and consumption reduction. Ultra-fine nanobubbles can significantly improve the utilization rate of oxidants like ozone—raising it from below 60% in traditional processes to over 95%, and cutting oxidant consumption by more than 40%. Its high-efficiency oxygen dissolution capacity can reduce the operational load of aeration equipment and lower power consumption. Meanwhile, it decreases chemical dosage, significantly reducing the operational costs of wastewater treatment and enhancing the economic feasibility of the process.
In addition, the ultra-fine nanobubble technology does not rely on complex catalyst or microbial systems, and is less affected by water quality fluctuations. It also eliminates secondary pollution issues such as heavy metal leaching, meeting the requirements specified in GB 8978-1996 Integrated Wastewater Discharge Standard for heavy metal emissions. Furthermore, this technology can reduce pollutant adhesion and scaling inside reactors, decrease equipment maintenance frequency and extend process operation cycles. Compared with conventional processes, it features significantly improved operational stability, with a service life extendable to over 5 years (vs. the industry average of 2–3 years).

PiC 2. Micro-bubbles in the Water
III. Summary
Sinokle Technology's independently developed ultra-fine nanobubble generation technology, relying on its core advantages such as ultra-high specific surface area, superior mass transfer efficiency, and wide water quality adaptability, has comprehensively optimized the wastewater treatment process in multiple dimensions including the depth of pollutant removal, process application scope, operational economy, and stability.
This technology not only effectively solves the treatment challenges of industrial wastewater with refractory organics, high salinity, and high load but also significantly reduces treatment energy consumption and costs. Conforming to the development trend of green environmental protection, it provides an efficient and sustainable technical solution for the advanced treatment of industrial wastewater and boasts broad application prospects.

